Univ.-Prof.in Mag.a Dr.in Maria Sibilia
ZentrumsleiterinGruppenleiterin
T: +43 (0)1 40160-57501 oder +43 (0)1 40160-57502
F: +43 (0)1 40160-957502
maria.sibilia@meduniwien.ac.at
X: @sibilia_maria
ORCID: 0000-0001-6129-5613
Forschungsschwerpunkt
Tumore werden zunehmend als Organe erkannt, die aus Krebszellen und einer Vielzahl von Zellen bestehen, die die „Tumormikroumgebung“ bilden, darunter Immunzellen, Gefäßzellen und Fibroblasten. Diese Stromazellen tragen wesentlich zur malignen Progression bei.
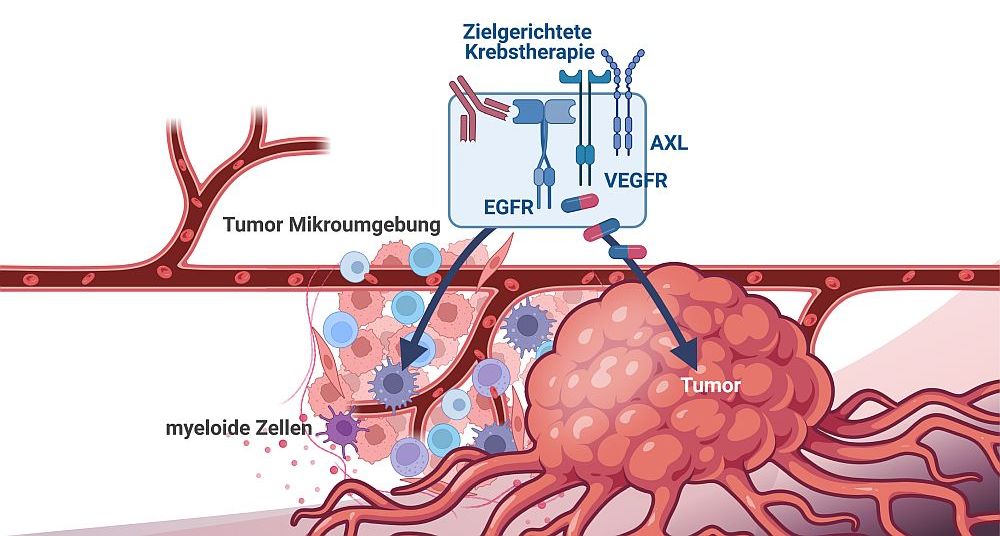
Anhand der Maus als Modellsystem wollen wir die Rolle des epidermalen Wachstumsfaktorrezeptors (EGFR) in Krebszellen, in Tumorstromazellen und deren komplexe Interaktion verstehen. Das ultimative Ziel ist es, dieses Wissen auf menschliche Patient:innen zu übertragen, um rationale und wirksame Therapien für die Behandlung von menschlichem Krebs zu entwickeln.
Ausgewählte Publikationen
The AP-1 transcription factors c-Jun and JunB are essential for CD8α conventional dendritic cell identity.
Novoszel P, Drobits B, Holcmann M, Fernandes CS, Tschismarov R, Derdak S, Decker T, Wagner EF, Sibilia M.
Cell Death Differ. 2021 Aug;28(8):2404-2420. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00765-4. Epub 2021 Mar 23.
Psoriatic skin inflammation is promoted by c-Jun/AP-1-dependent CCL2 and IL-23 expression in dendritic cells.
Novoszel P, Holcmann M, Stulnig G, De Sa Fernandes C, Zyulina V, Borek I, Linder M, Bogusch A, Drobits B, Bauer T, Tam-Amersdorfer C, Brunner PM, Stary G, Bakiri L, Wagner EF, Strobl H, Sibilia M.
EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Apr 9;13(4):e12409. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202012409. Epub 2021 Mar 16.
Hair eruption initiates and commensal skin microbiota aggravate adverse events of anti-EGFR therapy.
Jörg Klufa, Thomas Bauer, Buck Hanson, Craig Herbold, Philipp Starkl, Beate Lichtenberger, Dagmar Srutkova, Daniel Schulz, Igor Vujic, Thomas Mohr, Klemens Rappersberger, Bernd Bodenmiller, Hana Kozakova, Sylvia Knapp, Alexander Loy, Maria Sibilia;
Sci Transl Med. 2019 Dec 11;11(522):eaax2693. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax2693.
EGFR in Tumor-Associated Myeloid Cells Promotes Development of Colorectal Cancer in Mice and Associates With Outcomes of Patients.
Srivatsa S, Paul MC, Cardone C, Holcmann M, Amberg N, Pathria P, Diamanti MA, Linder M, Timelthaler G, Dienes HP, Kenner L, Wrba F, Prager GW, Rose-John S, Eferl R, Liguori G, Botti G, Martinelli E, Greten FR, Ciardiello F, Sibilia M.;
Gastroenterology. 2017 Jul;153(1):178-190.e10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.053. Epub 2017 Apr 9.
EGFR is required for FOS-dependent bone tumor development via RSK2/CREB signaling.
Linder M, Glitzner E, Srivatsa S, Bakiri L, Matsuoka K, Shahrouzi P, Dumanic M, Novoszel P, Mohr T, Langer O, Wanek T, Mitterhauser M, Wagner EF, Sibilia M.;
EMBO Mol Med. 2018 Nov;10(11). pii: e9408. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201809408.
EGFR has a tumour-promoting role in liver macrophages during hepatocellular carcinoma formation.
Lanaya H, Natarajan A, Komposch K, Li L, Amberg N, Chen L, Wculek SK, Hammer M, Zenz R, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Sieghart W, Trauner M, Wang H, Sibilia M.;
Nat Cell Biol. 2014 Oct; 16(10):972-81, 1-7.
Epidermal EGFR controls cutaneous host defense and prevents inflammation.
Lichtenberger BM, Gerber PA, Holcmann M, Buhren BA, Amberg N, Smolle V, Schrumpf H, Boelke E, Ansari P, Mackenzie C, Wollenberg A, Kislat A, Fischer JW, Röck K, Harder J, Schröder JM, Homey B, Sibilia M.;
Sci Transl Med. 2013 Aug 21; 5(199):199
Imiquimod clears tumors in mice independent of adaptive immunity by converting pDCs into tumor-killing effector cells.
Drobits B, Holcmann M, Amberg N, Swiecki M, Grundtner R, Hammer M, Colonna M, Sibilia M.;
J Clin Invest. 2012 Feb 1; 122(2):575-85.
Autocrine VEGF signaling synergizes with EGFR in tumor cells to promote epithelial cancer development.
Lichtenberger BM, Tan PK, Niederleithner H, Ferrara N, Petzelbauer P, Sibilia M.;
Cell. 2010 Jan 22; 140(2):268-79.
Alle Publikationen
Vorstellung Maria Sibilia, Robert Eferl, Martin Filipits

Nach der Aktivierung werden Daten an YouTube übermittelt. Weitere Infos hier: Datenschutzerklärung
Immunforschung für verbesserte Krebstherapien

Nach der Aktivierung werden Daten an Vimeo übermittelt. Weitere Infos hier: Datenschutzerklärung
Förderungen
Der Standard: Edition Zukunft - 29.4.2022
Wie können wir Krebs endlich heilen?
Podcast:
Gast: Maria Sibilia
Moderation: Florian Koch, Jakob Pallinger
